Flask

Flask Intro..
Creating a Virtual env in Ubuntu
Open terminal and type the following command
python3 -m venv name_of_virtual_envMaking a virtual environment named ‘Flask_tutorial’
python3 -m venv Flask_tutorialActivating the virtual environment
source Flask_tutorial/bin/activateInstalling Flask
pip3 install user flaskHello Flask
#imports Flask from the package flask
from flask import Flask
#This creates an instance of the Flask object using #our module's name as a parameter.
#Flask uses this to resolve resources
app = Flask(__name__)
#Following line is python decorator.
#Flask uses decorators for URL routing, so this line #of code means that the function directly below it #should be called whenever a user visits the main #root page of our web application.
@app.route("/")
#Following line define a function and returns our #message.
def index():
return "I am learning Flask"
#Following line is a simple conditional statement #that evaluates to True if our application is run #directly.
#It is used to prevent Python scripts from being #unintentionally run when they are imported into #other Python files.
if __name__ == '__main__':
#This line kicks off Flask's development server #on our local machine. We set it to run on port 5000 #and set debug to True, which will help us see #detailed errors directly in our web browser.
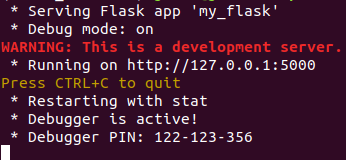
app.run(port=5000,debug=True)We save above program as ‘my_flask.py’ and type following command in terminal to run the above program.
python3 my_flask.pyOutput

pontu
0
Tags :